Aug 2024 – Nasim Najjarzadeh (PhD), Marketing Manager
Introduction:
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a vital component in the world of biochemistry and molecular biology research. At TdB Labs, we pride ourselves on offering high-quality FITC, both as a stand-alone dye and conjugated to dextran and other polysaccharides. In this article, we delve into the unique properties and applications of FITC, highlighting why it is one of our most important products.
About FITC
- FITC is a derivative of fluorescein, a synthetic organic compound. It is widely used as a fluorescent labeling reagent due to its ability to emit bright green fluorescence when excited by blue light. This makes it an invaluable tool in various scientific applications.
- FITC is extensively utilized for labeling proteins, antibodies, peptides, hormones, amine-modified oligonucleotides, and various other amine-containing molecules. The isothiocyanate group (-N=C=S) in FITC interacts with amino-terminal and primary amine groups on target biomolecules, forming stable covalent thiourea bonds. These fluorescein conjugates serve as specific probes in various applications, such as enzymatic kinetics, immunocytochemistry, immunohistochemistry, fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (1)
- FITC is not cell permeable. As an isothiocyanate derivative of fluorescein, it cannot cross the intact membranes of live cells (2).
- FITC is sensitive to both temperature and pH. The fluorescent signal intensity of FITC-labeled conjugates significantly decreases in more acidic environments. For instance, the intensity of FITC-dextran drops by over 95% when the pH is lowered from 10 to 3. Additionally, FITC is unstable at elevated temperatures, and conjugates made with FITC are prone to hydrolysis of the fluorescein label.
Structure and Chemical Properties of FITC
FITC (Fluorescein isothiocyanate) is a fluorescent dye with an excitation maximum at λ = 495 nm and an emission maximum at approximately λ = 519 nm. The compound appears yellow, while the emitted light is green. FITC exists in two isomeric forms:
- Isomer I: Also known as fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate or 5-FITC
- Isomer II: Also known as fluorescein 6-isothiocyanate or 6-FITC
The variation in excitation and emission wavelengths between the two isomers is minor. FITC-functionalized biopolymers, such as FITC-dextrans, exhibit similar excitation and emission properties.
Depending on the isomer, FITC contains an isothiocyanate group at either position 5 (isomer I) or position 6 (isomer 2) of the bottom benzene ring, see Figure 1. Isothiocyanate easily reacts with nucleophiles such as amines under mild conditions. The compound is often used in the form of one of its two isomers or sometimes as a mixture of the two.a
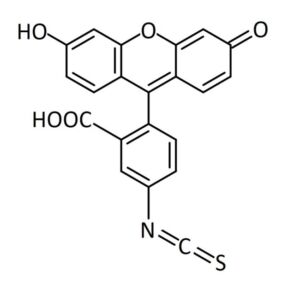
Fig 1. Structural representation of FITC isomer I. FITC isomer I (fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate) contains an isothiocyanate group at position 5.
Applications of FITC
- Flow Cytometry: FITC is commonly used to label antibodies in flow cytometry, allowing researchers to analyze cells’ physical and chemical characteristics. The bright fluorescence of FITC enables the detection of specific cell populations and the measurement of various cellular parameters, such as size, granularity, and protein expression levels.
- Fluorescence Microscopy: In fluorescence microscopy, FITC-conjugated molecules help visualize cellular structures and processes with high specificity and sensitivity. FITC’s fluorescence can be easily distinguished from other fluorophores, making it ideal for multi-colour imaging experiments.
- Immunoassays: FITC is frequently used in immunoassays to detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies, aiding in diagnostics and research. The high sensitivity of FITC-based assays allows for the detection of low-abundance targets, making them valuable tools in clinical and research settings.
FITC Conjugates: At TdB Labs, we offer FITC conjugated to dextran and other polysaccharides. These conjugates enhance the versatility of FITC, enabling its use in a broader range of applications. Dextran conjugates, for example, are particularly useful in studying cellular uptake and trafficking, as well as in drug delivery research. The hydrophilic nature of dextran improves the solubility and biocompatibility of FITC conjugates, making them suitable for in vivo studies.
FITC-products from TdB Labs
- FITC (isomer I)
- FITC -dextran
- FITC -lysine-dextran
- FITC-CM -dextran
- FITC-CM -polysucrose
- FITC-DEAE -dextran
- FITC-DEAE -polysucrose
- FITC -dextran sulfate
- FITC -hydroxyethyl starch
- FITC -inulin
- FITC -polysucrose
- FITC -Q-dextran
- FITC -trehalose
- Fluorescein Hyaluronic Acid
Read more about it on our website.
Why Choose TdB Labs’ FITC?
Our FITC products are known for their high purity and consistent performance. We ensure rigorous quality control to provide researchers with reliable and reproducible results. Whether you need FITC as a stand-alone dye or as part of a conjugate, TdB Labs is your trusted partner in scientific research.
Conclusion
FITC remains a cornerstone in the toolkit of many researchers. Its versatility and reliability make it an essential dye in various scientific fields. At TdB Labs, we are committed to supporting your research with top-quality FITC products. Explore our range today and see the difference for yourself.
References
- The, T. H., & Feltkamp, T. E. (1970). Conjugation of fluorescein isothiocyanate to antibodies. I. Experiments on the conditions of conjugation. Immunology, 18(6), 865-873
- Perfetto, S. P., Chattopadhyay, P. K., Lamoreaux, L., Nguyen, R., Ambrozak, D., Koup, R. A., & Roederer, M. (2010). Amine-reactive dyes for dead cell discrimination in fixed samples. Current protocols in cytometry, Chapter 9, Unit-9.34. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142956.cy0934s53
- Ma, L. Y., Wang, H. Y., Xie, H., & Xu, L. X. (2004). A long lifetime chemical sensor: study on fluorescence property of fluorescein isothiocyanate and preparation of pH chemical sensor. Spectrochimica acta. Part A, Molecular and biomolecular spectroscopy, 60(8-9), 1865-1872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2003.10.004